FAQ's
What is IV Hydration?
IV Hydration is the administration of nutrients and hydration directly into the bloodstream and represents the most powerful form of nutritional medicine available. IV hydration bypasses the gastrointestinal tract and delivers 100% absorption of nutrients resulting in an immediate and profound cellular metabolism and function throughout the body.

What is Diabetes?
A group of diseases that results in too much sugar in the blood.
What are symptoms of Type I and Type II Diabetes?
– thirst
– frequent urination
– hunger
– fatigue
– blurred vision
How can you prevent Diabetes?
– healthy diet
– no smoking
– drink water
– exercise regularly

Who can get Type 2 Diabetes?
The following people are higher at risk for Type 2 diabetes diagnosis:
• Have a history of gestational diabetes
• Have a history of type 2 diabetes in their family
• Have prediabetes
• Have low HDL cholesterol or high triglycerides
• Have high blood pressure
• Do not exercise
• Are obese or overweight
• Are over 45 years
• Are members of certain racial or ethnic groups including:
African Americans
Asian Americans/ Pacific Islanders
Latinos
Native Americans
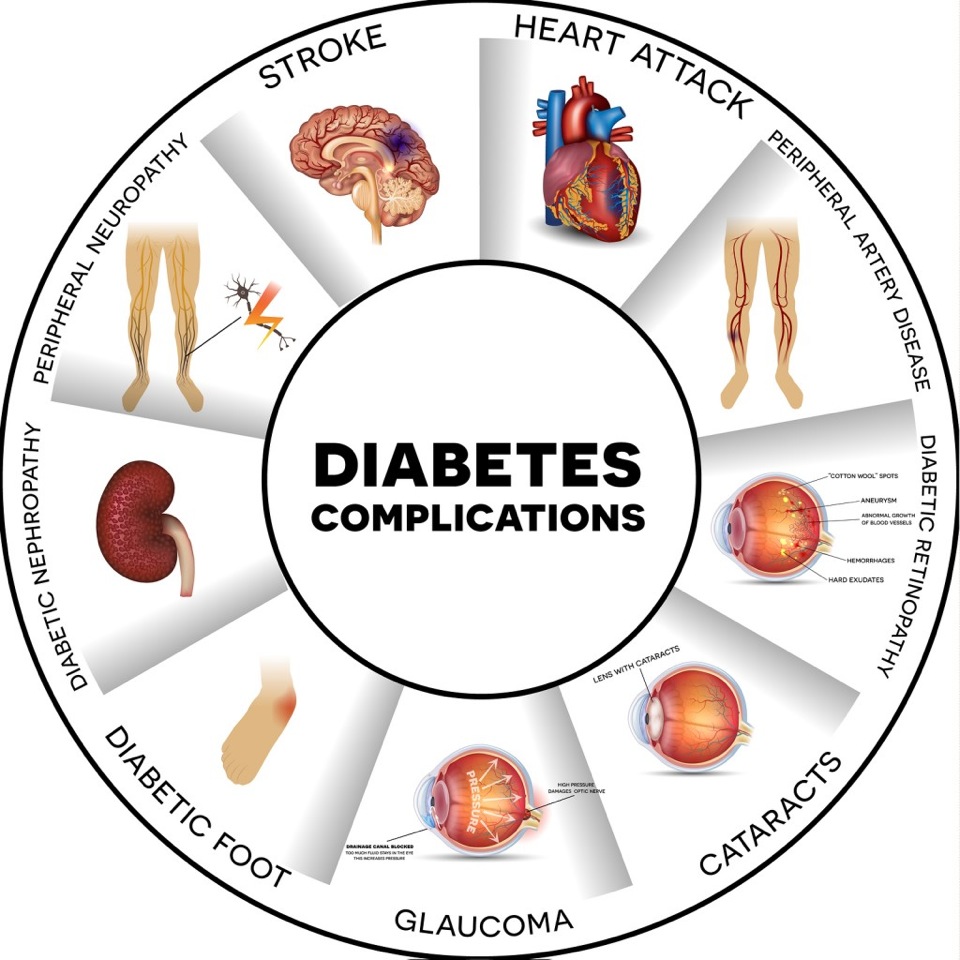
Complications resulting from Type 2 Diabetes
When Type 2 diabetes is not properly controlled, serious or life threatening problems may occur, which may include:
Retinopathy– It is essential to control blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol to prevent eye disease from getting worse.
Kidney damage– The longer you have diabetes, the greater you are at risk of kidney disease. Kidney damage can lead to kidney failure if not caught early.
Is Cholesterol Important
The higher your blood cholesterol, the greater your risk for heart attack or stroke. That’s why you need to know your cholesterol level. If it’s high, you can take steps to bring it down. Eating the right foods and getting enough exercise can help. Some people also need medication to control their cholesterol. Your healthcare provider can help you get started on a plan to control your cholesterol
What are problems associated with high blood pressure?
– heart disease
– kidney disease
– stroke
– eye disease
– atherosclerosis

What is normal blood pressure?
– systolic pressure less than 120
– diastolic less than 80 mmHg
What causes high blood pressure?
– inactivity
– poor diet
– obesity
– older age
– genetics